An endodontic evaluation is a comprehensive examination of a tooth by an endodontist, a dental specialist who focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of problems related to the tooth pulp and roots. The pulp is the soft tissue inside the tooth that contains nerves, blood vessels, and connective tissue.
The goal of an endodontic evaluation is to determine the health of the tooth pulp and diagnose any problems that may be present. This information is essential for developing a treatment plan to address the issue and save the tooth whenever possible.
Six Steps of Endodontic Evaluation
Let’s now explore the engaging six-step process involved in endodontic evaluation:
Step 1: Patient History
Before proceeding with the evaluation, the dentist gathers comprehensive information about the patient’s dental history, including past treatments, symptoms, and any relevant medical conditions.
Step 2: Clinical Examination
The dentist conducts a thorough examination of the oral cavity, assessing the condition of the teeth, gums, and surrounding tissues. Special attention is given to areas of discomfort or abnormalities.
Step 3: Radiographic Evaluation
Dental X-rays are taken to visualize the internal structures of the teeth and detect any underlying issues such as decay, infections, or structural abnormalities.
Step 4: Diagnostic Tests
Various diagnostic tests, such as pulp vitality tests and percussion tests, are performed to assess the health of the dental pulp and surrounding tissues. These tests help in determining the need for further treatment.
Step 5: Diagnosis
Based on the findings from the clinical examination, radiographic evaluation, and diagnostic tests, the dentist formulates a diagnosis and discusses treatment options with the patient.
Step 6: Treatment Planning
Once a diagnosis is established, the dentist develops a customized treatment plan tailored to address the patient’s specific needs and preferences. This may include procedures such as root canal therapy, dental restorations, or surgical interventions.
Significance of Endodontic Evaluation
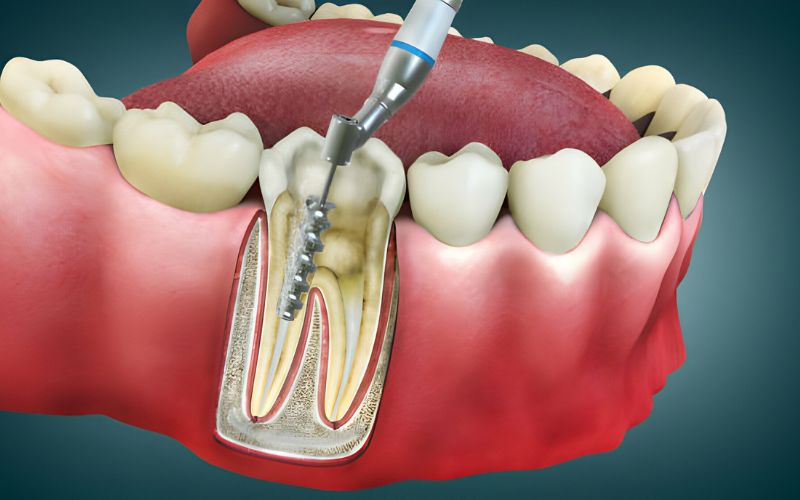
Endodontic evaluation serves as a cornerstone in preventive dental care. By undergoing regular evaluations, individuals can detect dental issues early, preventing further complications and ensuring timely treatment.
Preventive Dental Care
Regular endodontic evaluations are essential for early detection and management of dental issues, significantly those necessitating root canal treatment. These evaluations serve a dual purpose: they ensure the ongoing integrity of previous dental work and pinpoint areas at risk for future problems, including those that might require root canal treatment. This proactive approach is key to maintaining optimal oral health, as it allows for the timely intervention of root canal therapy to preserve natural teeth and prevent the spread of infection.
Early Detection of Dental Issues
Endodontic evaluations enable the early detection of conditions such as pulpitis, dental abscesses, and cracked teeth. Timely intervention not only alleviates discomfort but also preserves the affected tooth, avoiding the need for more invasive treatments.
Importance in Treatment Planning
Accurate diagnosis through endodontic evaluation is pivotal in devising effective treatment plans. By thoroughly assessing the condition of the tooth and surrounding tissues, dentists can tailor treatment strategies to address specific patient needs.
Components of Endodontic Evaluation
A comprehensive endodontic evaluation typically comprises three main components: clinical examination, radiographic evaluation, and diagnostic tests.
Clinical Examination
During their thorough check-ups, dentists take a close look at your mouth, pinpointing any dental discomfort, inspecting soft tissues for any red flags of inflammation or infection, and taking a special interest in the health and performance of dental restorations like dental bridges. This meticulous examination is key to maintaining your mouth’s overall well-being and ensuring solutions like dental bridges are doing their job effectively.
Radiographic Evaluation
Radiographic evaluation involves the use of dental X-rays to visualize the internal structures of the teeth and surrounding tissues. Different types of radiographs provide valuable insights into the extent of dental decay, the presence of infections, and root morphology.
Diagnostic Tests
Various diagnostic tests, such as pulp vitality tests, percussion, and palpation, help determine the health status of the dental pulp and surrounding tissues. Additionally, advanced tools like electronic apex locators aid in accurately locating the root apex during endodontic procedures.
Common Findings in Endodontic Evaluation
Endodontic evaluations may reveal a range of dental conditions, including pulp necrosis, periapical lesions, and vertical root fractures.
Pulpal Necrosis
Pulpal necrosis refers to the death of dental pulp due to injury, decay, or infection. Symptoms include severe toothache, discoloration of the affected tooth, and swelling of the surrounding gums.
Periapical Lesions
Periapical lesions, also known as periapical granulomas or cysts, form at the apex of the tooth root in response to chronic inflammation or infection. These lesions may appear as radiolucent areas on dental X-rays and can cause localized pain and swelling.
Vertical Root Fractures
Vertical root fractures are cracks that extend longitudinally along the root of the tooth. These fractures often result from trauma or excessive stress on the tooth and may lead to tooth mobility, pain upon biting, and localized infection.
Learn About – Advantages and Disadvantages of Deep Teeth Clean
FAQs
What are the common symptoms that prompt an endodontic evaluation?
Persistent toothache, sensitivity to hot or cold, swelling or tenderness in gums, and discoloration of teeth are common symptoms that warrant an endodontic evaluation.
How often should one undergo an endodontic evaluation?
The frequency of endodontic evaluations depends on factors such as age, dental history, and risk factors for dental problems. Generally, individuals should undergo evaluations at least once a year as part of routine dental care.
Can endodontic evaluation detect hidden dental problems?
Yes, endodontic evaluations can detect hidden dental problems such as cracks, infections, and abnormalities in tooth structure that may not be visible during a routine dental examination.
What are the possible treatments recommended after an endodontic evaluation?
Depending on the diagnosis, treatments may include root canal therapy, apicoectomy (surgical removal of the tooth’s apex), or extraction. The choice of treatment aims to preserve the affected tooth and restore its function and aesthetics.
Conclusion
understanding endodontic evaluation and its procedures is crucial for anyone facing potential dental treatments. Personally, I found that diving into the specifics of each step helped alleviate much of the anxiety associated with dental work. Knowing what to expect—from the initial consultation to the final follow-up—can transform an intimidating experience into a manageable one. If you’re facing this type of dental care, remember that knowledge is power. Stay informed, ask questions, and trust that your endodontist’s goal is to help preserve your smile for years to come.